The technical concept of water cooling
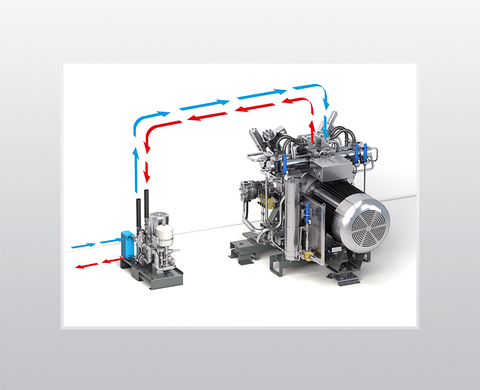
Water cooling has significant advantages over air cooling, as it supports installation even under the most difficult spatial and ambient conditions:
- The compressor block (intercooler and aftercooler, valve heads) is water-cooled separately
- Heat is dissipated efficiently
- Cooling of the valve heads reduces the thermal load to which the valves are exposed. Positive effects: prolonged valve service life and minimum wear
- Waste heat can be used for water for heating/washing
- Oil consumption is reduced
- Operational reliability and service life increase
- The noise level of the compressor unit is much lower than that of an air-cooled compressor
- Only minimum ventilation of the room is required to dissipate the heat from the motor and the residual heat from the compressor
"Hybrid cooling" combines all of the advantages of air and water cooling. As in a motor vehicle, the block itself is primarily water-cooled: this is done deliberately with heat dissipation in mind. A heat exchanger is connected to cool the cooling water with ambient air.
This system is independent of the on-site cooling water supply and can even be installed in locations where there is no cooling water or the supply of cooling air available for the compressor is limited.
